Microdochium poae
| Authors |
J.M. Liang & Lei Cai 2019 |
| Strain |
14104 |
| Classification |
Xylariales, Microdochiaceae, Microdochium |
| Culture collection |
BCRC FU31177 |
| Detection frequency |
Low |
| Figure |
 Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA 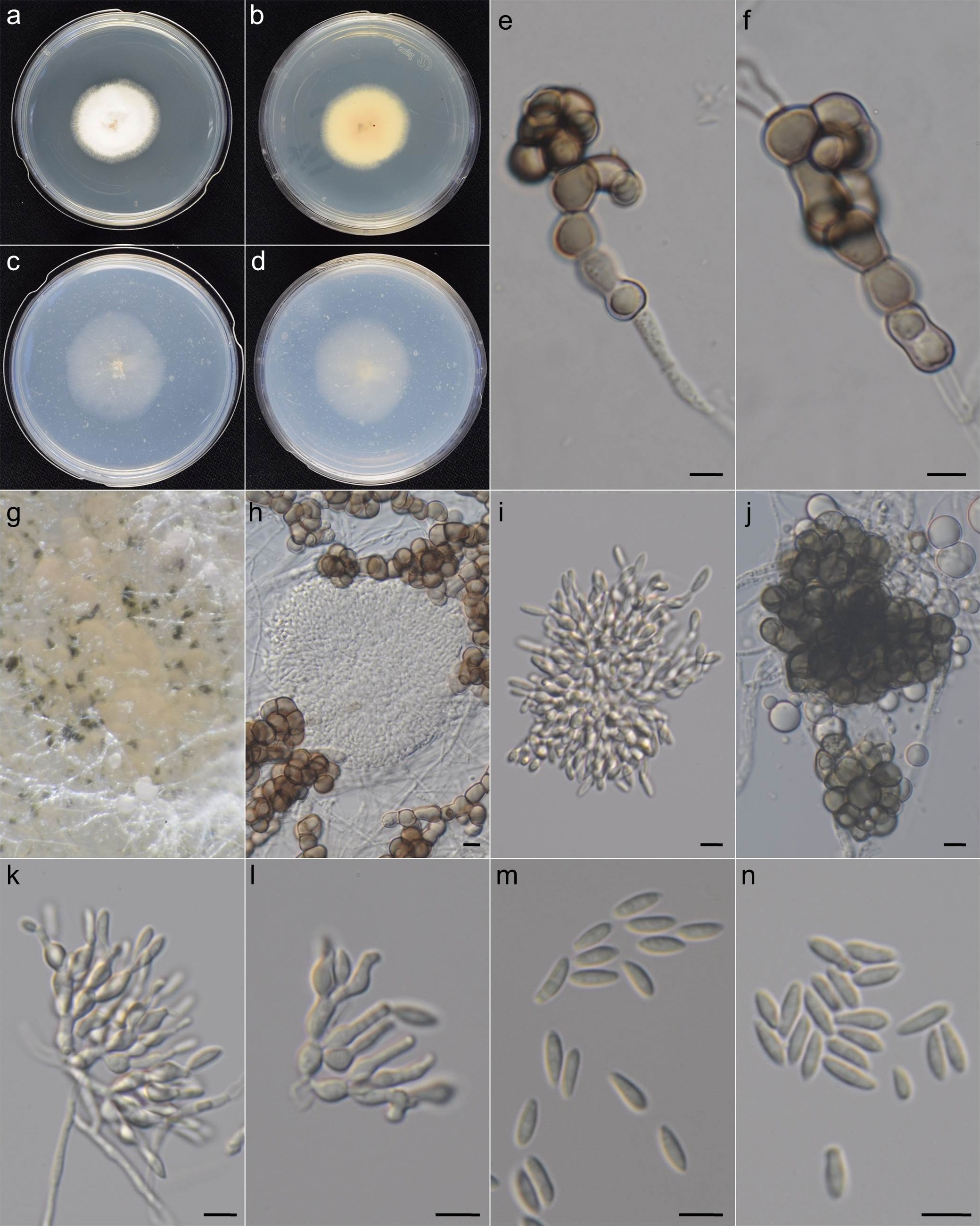 Fig. 2 Microdochium poae. a–d. Colonies at 25 °C after 5 d. a–b. PDA. c–d. OA. e–f. Chlamydospores. g–h. Sporodochia and chlamydospores on OA media. i, k. Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia. l. Conidiogenous cells with annellated necks j. Microsclerotia forming by aggregation of chlamydospores. m–n. Conidia (Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified) Fig. 2 Microdochium poae. a–d. Colonies at 25 °C after 5 d. a–b. PDA. c–d. OA. e–f. Chlamydospores. g–h. Sporodochia and chlamydospores on OA media. i, k. Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia. l. Conidiogenous cells with annellated necks j. Microsclerotia forming by aggregation of chlamydospores. m–n. Conidia (Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified) |
| Colonies |
Colonies on PDA attaining 15-, 21-, 24-, 20-, 20-mm under 16°C, 20 °C, 24 °C, 28 °C, 32 °C after 5 days, respectively, floccose with abundant white aerial mycelium, center turn pale orange with age, sporulation scanty. Reverse pale orange, darkening with age (> 4 wk) due to the formation of chlamydospores, slightly zonate. Colonies on OA effuse, aerial mycelium moderate, white, slighty zonate, reverse similar, scattered, dark brown chlamydospores produced with age (> 2 wk). |
| Sporodochia |
Sporodochia present, mostly superficial, slimy, pale orange. |
| Conidiophores |
Sporodochial conidiophores macronematous or micronematous, hyaline, short, slightly thicker than vegetative hyphae, 2–3.5 μm in width. |
| Conidiogenous cells |
Sporodochial conidiogenous cells discrete, hyaline, flask-shaped, laterally or terminally, often in whorls, annellidic, 5.0–7.0 × 2.0–3.0 μm, necks often elongated, with several annellations when aged. |
| Conidia |
Sporodochial conidia slimy, hyaline, fusiform or obovate, straight or slightly curved, base often slightly truncated, 5.5–7.5 × 2.0–3.0 μm. |
| Chlamydospores |
Chlamydospores present in aged culture, globose, subglobose, cylindrical or irregular, intercalary or terminal, thick-walled, brown to dark olivaceous, 4.0–8.0 × 4.0–13.0 μm. |
| Sclerotia |
Microsclerotia present, forming by aggregation of chlamydospores. |
| Note |
Microdochium poae resembles Microdochium bolleyi, another chlamydospore-producing Microdochium, but differs in having annellidic conidiogenous cells. Compared with the strain obtained in this study, Microdochium poae grew faster (40–45 mm / 1 wk) on OA medium in the original description (Liang et al. 2019). The difference in the growth rate could be attributed to the difference in the composition of OA. The OA used in this study was made up of 3% oatmeal in distilled water following the usage of Hernández-Restrepo et al. (2016), while the OA used by Liang et al. (2019) was prepared with 6% oatmeal. The ITS, TUB, RPB2 sequences of Microdochium poae 14104 (BCRC FU31177) obtained in this study were identical to Microdochium poae CGMCC3.19170 (ex-type). LSU region for CGMCC3.19170 was not available. |
| Pathogenicity |
Unknown |
| Specimens examined |
Taiwan, Ilan County, rice grains, Aug 2014, Jie-Hao Ou, 14104 |
| ITS |
TCTCCAAACCATGTGAACTTACCACTGTTGCCTCGGTGGTTTGGGTCTTCGGGCCTGACCACCGGCGGACTACTAAACTCTTGTTAATTTTTGGCATTCTGAATCATAACTAAGAAATAAGTTAAAACTTTCAACAACGGATCTCTTGGTTCTGGCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGCGAAATGCGATAAGTAATGTGAATTGCAGAATTCAGTGAATCATCGAATCTTTGAACGCACATTGCGCCCATTAGTATTCTAGTGGGCATGCCTGTTCGAGCGTCATTTCAACCCTTAAGCCTAGCTTAGTGTTGGGAGACTGCCTAATACGCAGCTCCTCAAAACCAGTGGCGGAGTCTGTTCGTGCTCTGAGCGTAGTAATTCTTTATCTCGCTTCTGCAAGCCGATTAGACAACAGCCATAAACCGCACCCTTCGGGGGCACTTTTTAATGGTTGACCTCGGATCAGGTAGGAATACCCGCTGAACTTAA |
 Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA
Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA  Fig. 2 Microdochium poae. a–d. Colonies at 25 °C after 5 d. a–b. PDA. c–d. OA. e–f. Chlamydospores. g–h. Sporodochia and chlamydospores on OA media. i, k. Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia. l. Conidiogenous cells with annellated necks j. Microsclerotia forming by aggregation of chlamydospores. m–n. Conidia (Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified)
Fig. 2 Microdochium poae. a–d. Colonies at 25 °C after 5 d. a–b. PDA. c–d. OA. e–f. Chlamydospores. g–h. Sporodochia and chlamydospores on OA media. i, k. Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia. l. Conidiogenous cells with annellated necks j. Microsclerotia forming by aggregation of chlamydospores. m–n. Conidia (Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified)