Microascus gracilis
| Authors |
(Samson) Sand.-Den., Gené & Guarro 2015 |
| Strain |
13005 |
| Classification |
Microascales, Microascaceae, Microascus |
| Culture collection |
BCRC FU30165 |
| Detection frequency |
Low |
| Accession number |
LC494378 |
| Figure |
 Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA 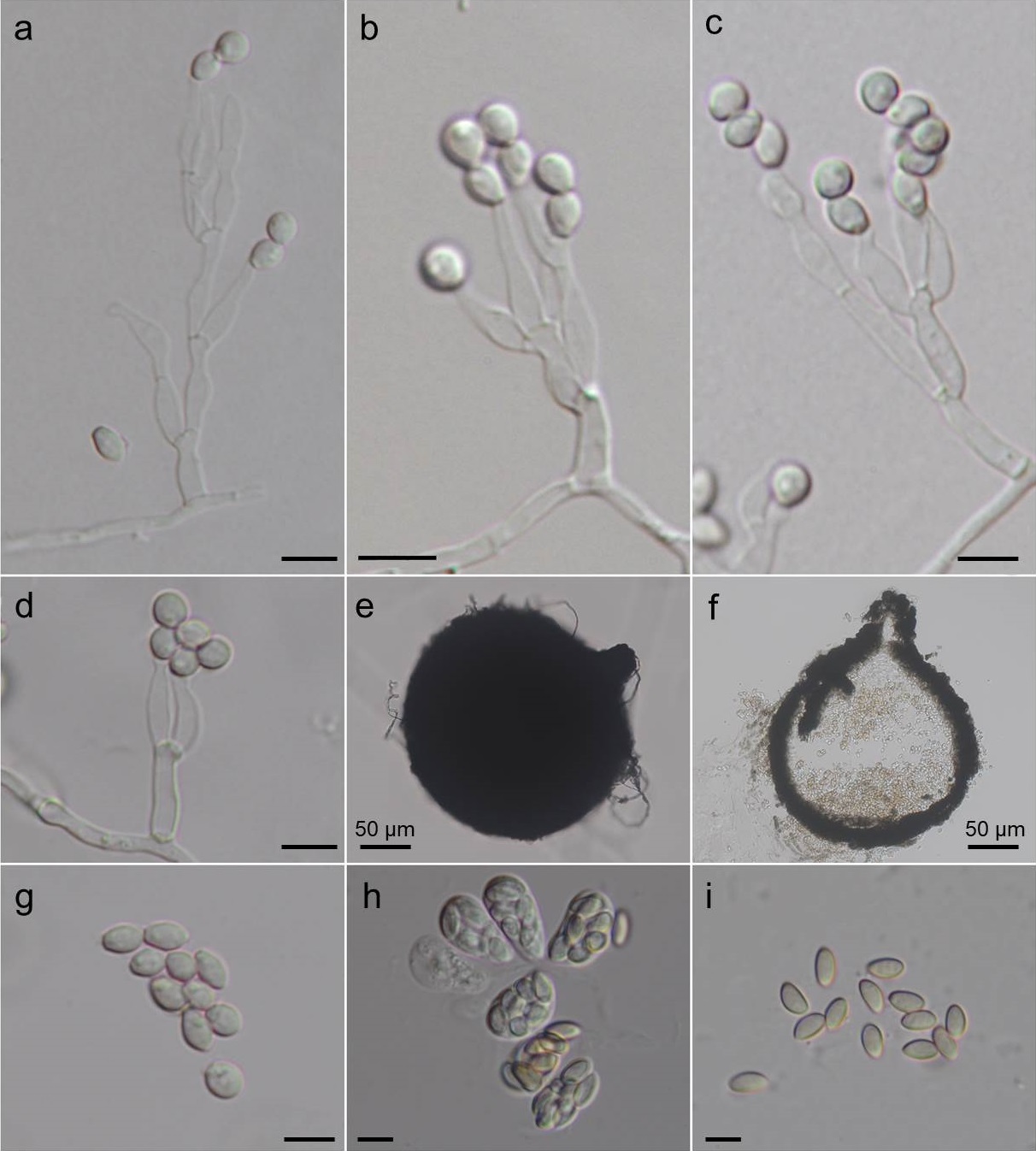 Fig. 2 Microascus gracilis. a–d. Conidiophores and conidia. e, f. Perithecia. g. Conidia. h. Asci. i. Ascospores(Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified) Fig. 2 Microascus gracilis. a–d. Conidiophores and conidia. e, f. Perithecia. g. Conidia. h. Asci. i. Ascospores(Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified) |
| Colonies |
Colonies on PDA slow growing, attaining less than 10-mm at 25 °C after 5 days, grey, slightly funiculose neat the center, reverse dark grey. |
| Conidiophores |
Conidiophores marconematous, subhyaline, simple or branch, 7–20 × 2–3 µm. |
| Conidiogenous cells |
Conidiogenous cells discrete, cylindrical, annellidic, 7–14 × 1–2.5 µm. |
| Conidia |
Conidia catenate, pale brown, globose or oblong with truncated base, 3.5–5 × 2.5–3.5. |
| Ascomata |
Perithecia black, subspherical, 170–240 µm in diameter, necks up to 100 µm. |
| Asci |
Asci ovoid, containing 8 ascospores, 11–15 × 6–9 µm. |
| Ascospores |
Ascospores obovoid, fusiform or reniform, pale brown to golden brown, 5–6.5 × 2.5–3 µm. |
| Note |
This species was reported mainly from food and soils, and occasionally pathogenic to humans (Sandoval-Denis et al., 2013). Sexual and asexual state, Scopulariopsis state, can both occur in the same culture medium. Strain 13005 shares 99.71% identity in ITS region with the ex-type strain of Microascus gracilis(CBS 369.70, LM652412). |
| Pathogenicity |
Unknown |
| Specimens examined |
Taiwan, Tainan City, rice grains (cultivar Tainan 11), Jan 2013, Jie-Hao Ou, 13005 |
| ITS |
GAACGCAGCGAAATGCGATAAGTAATGCGAATTGCAGAATTCAGTGAATCATCGAATCTTTGAACGCACATTGCGCCCGGCAGCAATCTGCCGGGCATGCCTGTCCGAGCGTCATTTCTGCCCTCGAGCGCGGTTCGGCCCCTAGCGGGCCGTCCGCCGCCCGGTGTTGGGGCGCTGCGGGCCCTCGTGCCCGCAGGCCCTGAAATGAAGTGGCGGTCCCGCCGCGGCGCCCCCTGCGTAGTAGTAAAGCACCTCGCATCGGGTCCCGGCGGAGGCCAGCCGTCGAACCTCTTTCTCTTGATGGTTTGACCTCGGATCAGGTAGGGTTACCCGCTGAACTTAA |
 Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA
Fig. 1 5-day-old colony on PDA  Fig. 2 Microascus gracilis. a–d. Conidiophores and conidia. e, f. Perithecia. g. Conidia. h. Asci. i. Ascospores(Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified)
Fig. 2 Microascus gracilis. a–d. Conidiophores and conidia. e, f. Perithecia. g. Conidia. h. Asci. i. Ascospores(Bars= 5 μm, unless otherwise specified)